
Cancer research has entered the era of big data, generating massive genomic datasets that require powerful computational resources. Traditional local servers struggle to handle this scale, leading to the rise of Cloud Computing solutions.
The ISB Cancer Genomics Cloud (ISB-CGC), developed by the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) in collaboration with Google Cloud and CSRA Inc., is one of three Cancer Genomics Cloud (CGC) Pilots funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). It provides researchers with secure, scalable, and flexible access to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), TARGET, and other major cancer datasets, enabling advanced genomic analysis without infrastructure limitations.
By leveraging Cloud Computing, machine learning, and bioinformatics tools, ISB-CGC accelerates the discovery of cancer biomarkers, drug targets, and personalized treatments.
This blog explores how ISB-CGC is transforming cancer genomics research and making high-performance computing accessible to scientists worldwide.
How ISB-CGC is Transforming Cancer Research?
File-Based Analysis: Processing Large-Scale Genomic Data in the Cloud
Handling massive DNA and RNA sequencing datasets can be overwhelming, but ISB-CGC makes it seamless. Instead of downloading terabytes of BAM and FASTQ files, researchers can process them directly in the cloud using virtual machines and Google Cloud Pipelines. This means complex analyses like variant calling, RNA quantification, and antigen receptor analysis can run efficiently without expensive infrastructure. With parallel computing, these tasks that once took days can now be completed in hours, making cancer research faster and more accessible than ever.
Query-Based Analysis: Turning Genomic Data into Actionable Insights
Beyond raw sequencing data, cancer research relies on structured insights—mutation patterns, gene expression profiles, and copy number variations. ISB-CGC organizes these high-level datasets into searchable tables, accessible through SQL, Python, and R. Researchers can instantly filter, compare, and analyze cancer data across multiple studies, integrating reference databases like GENCODE, Ensembl, and COSMIC. With over 250,000 queries executed, this system empowers scientists to uncover patterns in cancer genomics at an unprecedented scale.
Web-Based Interactive Analysis: Exploring Data Like Never Before
For researchers who prefer a more visual and interactive approach, ISB-CGC provides a user-friendly web application. Imagine selecting a group of gastric cancer patients with a TP53 mutation, refining the dataset, and instantly retrieving relevant Whole Exome Sequencing (WXS) BAM files—all with a few clicks. The platform allows users to create custom cohorts, visualize trends, and analyze data in real time. Once ready, results can be stored in BigQuery for further AI-driven or statistical analysis, unlocking deeper insights into cancer treatment and precision medicine.
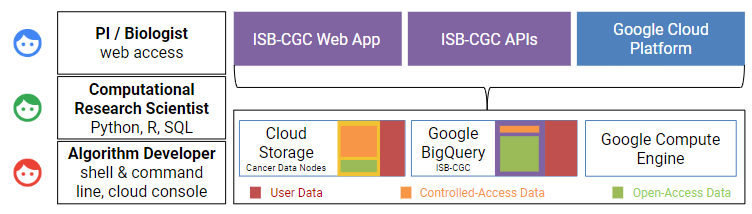
ISB-CGC System Architecture:
- Data as a Service (DaaS): Cancer genomics data stored in Google Cloud Storage and BigQuery for fast access and large-scale queries.
- Security and Authentication: Uses OAuth 2.0 and SAML for secure login and NIH credential verification.
- Interactive Access: Web-based tools for exploring, filtering, and visualizing genomic data.
- Programmatic Access: APIs allow automated data retrieval and analysis using SQL, Python, and R.
- Scalable Compute Power: Researchers can provision virtual machines (VMs) on demand, optimizing performance and cost.
- Integrated Tools and Documentation: Open-source code, tutorials, and seamless integration with Google Cloud services like BigQuery.
- Automatic Scaling and Load Balancing: Ensures efficient performance for handling large-scale datasets.
The Future of Cloud Computing in Cancer Genomics
Cloud computing is transforming cancer research by enabling scalable and collaborative data analysis. ISB-CGC’s data as a service model provides researchers with seamless access to genomic, clinical, and imaging data. As cloud adoption grows in initiatives like TOPMed and NIH’s Precision Medicine Initiative, interoperability between platforms will be crucial.
Looking ahead, ISB-CGC will continue to expand its capabilities in AI-driven analysis, multi-omics integration, and cross-platform data sharing, driving innovation in precision medicine and accelerating discoveries for better cancer treatments.
References
1. Reynolds, S. M., Miller, M., Lee, P., Leinonen, K., Paquette, S. M., Rodebaugh, Z., Hahn, A., Gibbs, D. L., Slagel, J., Longabaugh, W. J., Dhankani, V., Reyes, M., Pihl, T., Backus, M., Bookman, M., Deflaux, N., Bingham, J., Pot, D., & Shmulevich, I. (2017). The ISB Cancer Genomics Cloud: A Flexible Cloud-Based Platform for Cancer Genomics Research. Cancer research, 77(21), e7–e10. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0617